riskparam
riskparam solves optimization problem described in the section riskprog for several values of a parameter. The parameter is a component of a matrix or a vector in linear constraints, or a component of a vector in bounds on decision vector or a parameter in a risk function (e.g., confidence level in CVaR). Set of possible values of the parameter can be specified by some array of predefined values or by the number of points in the uniform grid in some interval of parameter values. riskparam plots optimal objectives vs. specified parameter values.
Mathematical Problem Statement
Finds a minimum for a problem specified by
![]()
subject to
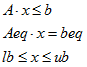
where
A, Aeq are matrices;
d, x are column vectors;
b, beq, lb, ub are column vectors or scalars;
risk is a PSG risk function, PSG deterministic function, or a PSG utility function (see List of PSG functions for riskparam).
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_El)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_E1,[],N_Par)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param, x0)
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string2, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param, x0, options)
Remarks
Omitted parameters should be substituted by square brackets “[]”.
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string)
This command can be used when the parameter is selected from the one-dimensional vector b or beq. The name of vector containing the parameter is specified by string. If a component of the vector b is selected as a parameter, then you should set string = 'b'; if a component of the vector beq is selected as a parameter, then you should set string = 'beq'. With this command the subroutine:
| • | Automatically determines lower and upper bounds of the interval of the selected parameter possible values; |
| • | Automatically generates ten equally spaced parameter values between the automatically calculated lower and upper bounds; |
| • | For each value of the selected parameter from the generated interval the subroutine minimizes |
| • | For ten parameter values riskparam optionally plots parameter vs. objective or objective vs. parameter (see description of options). There is also an option allowing to plot the graph with the parameter multiplied by -1 (output vector Parameters is also multiplied by -1). |
| • | This option is useful, for instance, in financial optimization, where you transform a constraint on the portfolio rate of return |
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1)
This command can be used when parameter is selected from multidimensional vector b or beq. These vectors should not be defined by a scalar constant (with the same constant value for all components of the corresponding vector). The parameter is the component number N_E1 in the vector specified by string2. This run automatically determines lower and upper bounds of the range of the selected parameter, and generates ten equally spaced parameter values between the lower and upper bounds.
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1,[],N_Par)
This command can be used when parameter is selected from multidimensional vector b or beq. These vectors should not be defined by a scalar constant (with the same constant value for all components of the corresponding vector). The parameter is the component number N_E1 in the vector specified by string. This run automatically determines lower and upper bounds of the range of the selected parameter, and generates N_Par equally spaced parameter values between the lower and upper bounds.
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par)
This command can be used when parameter is selected from matrices A, or Aeq, or vectors b, beq, lb, or ub, or when parameter of the risk function, w, is varied. If string2 ='A' or 'Aeq', then N_E1, and N_E2 specify the row and the column of parameter in the matrix specified by string. If string = 'b',or 'beq',or 'lb',or 'ub', then N_E1 specifies the parameter number in the vector specified by string, and N_E2 is ignored. If dimension of vector b, or beq, or 'lb',or 'ub', is greater than 1 and the vector is defined by a scalar constant (with the same constant value for all components of the vector), and the N_El is omitted, then the whole vector is changed. Low_Par, Up_Par specify lower and upper bounds of the range of the selected parameter. This run generates N_Par equally spaced parameter values between the lower and upper bounds and plots parameter values vs. optimal objectives.
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param)
The vector Param specifies a set of values of parameter for which run should be conducted. If Param is available, then N_Par, Low_Par, and Up_Par are ignored.
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param, x0)
Sets the starting point x0 for the problem with the smallest value of parameter. Problems with higher values of parameter may optionally use an optimal solution for problem with previous value of parameter as initial point (see description of options).
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle] = riskparam (risk, w, H, c, p, d, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub, string, N_E1,N_E2,N_Par, Low_Par, Up_Par, Param, x0, options)
Uses options specified in the structure options.
risk |
string with description of PSG function. For details on PSG functions see List of PSG functions for riskparam); |
w |
parameter (real) of the PSG function. If parameter is not present, then substitute parameter by square brackets “[]” ); |
H |
matrix for PSG function in objective risk; |
c |
vector of benchmark for one PSG function in objective risk. If the benchmark is not used, then substitute it by square brackets “[]”; |
p |
vector of probabilities for one PSG function in objective risk. If all probabilities are equal, you can substitute p by square brackets “[]”; |
d |
column vectors for linear component of objective; |
A |
matrix for linear inequality constraint; |
b |
vector or scalars for linear inequality constraint; |
Aeq |
matrix for linear equality constraint; |
beq |
vector for linear equality constraint; |
lb |
vector of lower bounds for x; |
ub |
vector of upper bounds for x; |
x0 |
initial point for x (see Initial Point); |
options |
structure that contains optimization options (see Options). |
Objectives |
row vector of the optimal values of the objective found by optimizing the problem for each parameter value; |
Parameters |
row vector parameter values; |
Points |
matrix of optimal points found by optimizing the problem for each parameter value. Each row is an optimal point corresponding to some parameter value; |
GraphHandle |
handle of the graphical object (if option.PlotGraph = ‘On’, otherwise GraphHandle = [] ). |
Structure options contains optimization options used by riskparam. The fields of the structure are:
Solver |
choose optimization PSG solvers from a list: VAN, CAR, BULDOZER, TANK (for more details see Optimization Solvers); |
Precision |
number of digits that solver tries to obtain in objective and constraints; |
Time_Limit |
time in seconds restricting the duration of the optimization process; |
Stages |
number of stages of the optimization process (this parameter should be specified for VaR, Probability, and Cardinality groups of functions). |
Linearization |
controls internal representation of risk function, which can speed up the optimization process (used with CAR and TANK solvers). 'On' or 'Off' (default) (see Linearizing); |
Path_to_Export_to_Text |
string with path to the folder for storing problem in General (Text) Format of PSG). If Path_to_Export_to_Text=‘’ (default) than the problem is not exported in General (Text) Format of PSG; |
Path_to_Export_to_MAT |
string with path to the folder for storing problem as mat-file. If Path_to_Export_to_MAT=‘’ (default) than the problem is not exported as mat-file. This option is intended for converting the problem to the PSG MATLAB Data Structure; |
IsInherit |
key specifying if a problem with the next value of parameter should use (IsInherit = 'On') an optimal solution of the problem with the previous value of parameter as an initial point (see Initial Point) or not (by the default IsInherit = 'Off'). |
Display |
key specifying if messages that may appear when you run this subroutine should be suppressed (Display = 'Off') or not (by the default: Display ='On') (see PSG Messages); |
Warnings |
key specifying if warnings that may appear when you run this subroutine should be suppressed (Warnings = 'On') or not (by the default: Warnings ='Off'); (see PSG Messages); |
PlotGraph |
key specifying if the graph should be built (PlotGraph = 'On') or not (by the default: PlotGraph ='Off'); |
PlotType |
key should be set to 1 for building objective vs. parameter plot, and 2 for building parameter vs. objective plot . Default PlotType = 1. |
ScaleParam |
scaling coefficients taking on a value from interval (-Infinity, +Infinity). Parameter is multiplied by ScaleParam when graph is building. Default ScaleParam = 1. |
ScaleObjective |
scaling coefficients taking on a value from interval (-Infinity, +Infinity). Objective is multiplied by ScaleObjective when graph is building. Default ScaleObjective = 1. |
Types |
specifies the variables types of a problem. If Types is defined as column-vector, it should include as many components as number of variables Problem includes. The components of column-vector can possess the values "0" - for variables of type real, or 1- for variables of type boolean, or 2 - for variables of type integer. If Types is defined as one number (0, or 1, or 2) than all variables types real, or boolean, or integer respectively. |
In this example we use the problem description similar to the defined in case study Basic CVaR Optimization Problem, Beyond Black-Litterman. This case study demonstrates a simple (basic) setup of a single-period portfolio optimization problem when risk is measured by CVaR. Efficient frontier (return vs. risk plot) is built.
Run the following example from the folder./Aorda/PSG/MATLAB/Examples/Problems/Example_Beyond_Black_Litterman_riskparam.m or type the next PSG problem in MATLAB:
load('ThisData');
N_Par = 20;
clear options;
options.PlotGraph = 'On';
options.PlotType = 2;
options.ScaleParam = -1;
format long;
[Objectives, Parameters, Points, GraphHandle]= riskparam ('cvar_risk', 0.95, Hmatr, [], [], [], dmatr', -0.00105, Aeqmatr, beqvec, lbvec, [], 'b', [],[],N_Par, [], [], [],[],options);
fprintf('Points: %d\n', length(Parameters));
fprintf('Parameters Objectives:\n');
fprintf('%f\t%f\n', [Parameters; Objectives]);
fprintf('Optimal Points:\n');
disp(Points);
You get the following output:
You get the following output:
Points: 20
Parameters Objectives:
0.000914 0.048190
0.000936 0.048713
0.000958 0.049634
0.000979 0.050673
0.001001 0.051820
0.001023 0.053095
0.001044 0.054479
0.001066 0.055929
0.001088 0.057451
0.001109 0.059042
0.001131 0.060698
0.001153 0.062415
0.001174 0.064190
0.001196 0.066014
0.001218 0.067875
0.001239 0.069778
0.001261 0.071742
0.001283 0.073766
0.001305 0.075861
0.001326 0.078182
Optimal Points:
0.4845 0.5155 0 0
0.4836 0.4585 0.0471 0.0108
0.4556 0.4299 0.0540 0.0605
0.4382 0.3853 0.0736 0.1028
0.4078 0.3627 0.0725 0.1570
0.3946 0.3063 0.1095 0.1895
0.3767 0.2657 0.1214 0.2362
0.3473 0.2283 0.1509 0.2735
0.3285 0.1887 0.1622 0.3205
0.2996 0.1691 0.1511 0.3803
0.2712 0.1392 0.1614 0.4282
0.2464 0.1044 0.1756 0.4735
0.2306 0.0710 0.1669 0.5315
0.1984 0.0519 0.1615 0.5882
0.1884 0.0012 0.1787 0.6316
0.1440 0 0.1596 0.6963
0.0892 0 0.1605 0.7503
0.0363 0 0.1572 0.8065
0 0 0.1184 0.8816
0 0 0.0004 0.9996
and the following graph with the efficient frontier
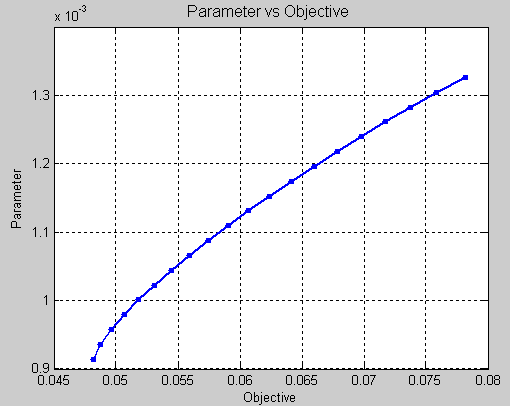
| • | Optimization Beyond Black Litterman |
| • | Portfolio Optimization, CVaR vs Standard Deviation. |
riskprog, riskconstrprog, riskcontparam, riskratioprog
List of PSG functions for riskprog
Subroutine riskparam works only with PSG functions described in this section.
Remarks
| • | Exponential Utility, Logarithmic Utility, Power Utility, Logarithms Sum, and Logarithms Exponents Sum functions are included in the objective with the negative coefficient -1 by default. However, you should not set any coefficient for these functions, riskparam sets it automatically. If risk function is a PSG risk, cardinality, or nonlinear function (except for Logarithms Sum and Logarithms Exponents Sum functions), then riskparam minimizes the objective |
| • | linear, pr_dev, pr_dev_g, pr_pen, and pr_pen_g PSG functions should NOT be combined with the vector d (substitute d by square brackets “[]” ). |
| • | Relative Entropy function (entropyr) can have up to 100,000,000 decision variables if Linearization='On' option is specified. This option may dramatically speedup calculations. In this case BULDOZER solver is recommended. |
The following PSG functions can be minimized by riskparam.
Full Name |
Brief Name |
Short Description |
|---|---|---|
avg |
Average Loss obtained by averaging Linear Loss scenarios, i.e., it is a linear function with coefficients obtained by averaging coefficients of Linear Loss scenarios. |
|
avg_g |
Average Gain obtained by averaging -(Linear Loss ) scenarios, i.e., it is a linear function with coefficients obtained by averaging coefficients of -(Linear Loss) scenarios. |
|
buyin |
For a finite dimension vector, buyin equals the number components satisfying two conditions: 1) absolute value of a component exceeds threshold_1; 2) if a component is positive, then its absolute value is below threshold_2, otherwise its absolute value is below threshold_3 |
|
buyin_neg |
Number of components of -(vector) exceeding threshold_1 and below threshold_2 |
|
buyin_pos |
Number of components of a vector exceeding threshold_1 and below threshold_2 |
|
cardn |
Number of absolute values of components of a vector exceeding some threshold |
|
cardn_neg |
Number of components of -(vector) exceeding some threshold |
|
cardn_pos |
Number of components of a vector exceeding some threshold |
|
cdar_dev |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio drawdown = d(j) = maxn ((uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) - (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). CDaR = CVaR Component Positive of vector (d(1), ..., d(J)) = average of the largest (1-α)% components of the vector (d(1), ..., d(J)), where 0≤α≤1 . |
|
cdar_dev_g |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio -drawdown = -d(j) = maxn (-(uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) + (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). CDaR for Gain = CVaR Component Positive of vector (-d(1), ...,- d(J)) = average of the largest (1-α)% components of the vector (-d(1), ..., -d(J)), where 0≤α≤1 . |
|
cvar_comp_neg |
Average of the largest (1-α)% of components of a -( vector), where 0≤α≤1 |
|
cvar_comp_pos |
Average of the largest (1-α)% of components of a vector, where 0≤α≤1 |
|
cvar_dev |
Conditional Value-at-Risk for (Linear Loss) - (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) , i.e., the average of largest (1-α)% of (Linear Loss) - (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) scenarios. |
|
cvar_dev_g |
Conditional Value-at-Risk for -(Linear Loss ) + (Average over scenarios Linear Loss) , i.e., the average of largest (1-α)% of - (Linear Loss) + (Average over scenarios Linear Loss) scenarios. |
|
cvar_risk |
Conditional Value-at-Risk for Linear Loss scenarios (also called Expected Shortfall and Tail VaR), i.e., the average of largest (1-α)% of Losses. |
|
cvar_risk_g |
Conditional Value-at-Risk for -(Linear Loss ) scenarios (also called Expected Shortfall and Tail VaR), i.e., the average of largest (1-α)% of -(Losses). |
|
drawdown_dev_avg |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio drawdown = d(j) = maxn ((uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) - (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). Drawdown Deviation = average of components of the vector (d(1), ..., d(J)) . |
|
drawdown_dev_avg_g |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio -(drawdown) = -d(j) = maxn (-(uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) + (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). Drawdown Average for Gain = average of components of the vector (-d(1), ...,- d(J)). |
|
drawdown_dev_max |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio drawdown = d(j) = maxn ((uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) - (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). Drawdown Maximum = Maximum Component Positive of vector (d(1), ..., d(J)) = largest component of the vector (d(1), ..., d(J)). |
|
drawdown_dev_max_g |
For every time moment, j=1,...J , portfolio -drawdown = -d(j) = maxn (-(uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment n ) + (uncompounded cumulative portfolio return at time moment j )). Drawdown Maximum for Gain = Maximum Component Positive of vector (-d(1), ...,- d(J)) = largest component of the vector (-d(1), ..., -d(J)). |
|
entropyr |
Relative entropy where probabilities are variables. |
|
exp_eut |
Exponential Utility function for Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
fxchg |
Sum of fixed changes for absolute values of components of a vector exceeding some thresholds |
|
fxchg_neg |
Sum of fixed changes for components of -(vector) exceeding some thresholds |
|
fxchg_pos |
Sum of fixed changes for components of a vector exceeding some thresholds |
|
linear |
Linear function with many variables |
|
log_eut |
Log Utility function for Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
log_sum |
Linear combination of logarithms of components of a vector |
|
logexp_sum |
Likelihood function in Logistic Regression |
|
max_comp_neg |
Maximal (largest) component of -(vector) |
|
max_comp_pos |
Maximal (largest) component of a vector |
|
max_dev |
Maximum of ((Linear Loss ) - (Average over Linear Loss scenarios)) scenarios. |
|
max_dev_g |
Maximum of (-(Linear Loss ) + (Average over Linear Loss scenarios)) scenarios.. |
|
max_risk |
Maximum of Linear Loss scenarios. |
|
max_risk_g |
Maximum of -(Linear Loss ) scenarios. |
|
meanabs_dev |
Mean Absolute Deviation for Linear Loss scenarios. |
|
meanabs_pen |
Mean Absolute for Linear Loss scenarios function. Calculated by averaging over scenarios the absolute values of losses . |
|
meanabs_risk |
Mean Absolute for Linear Loss scenarios. (Mean Absolute) =Average Loss + Mean Absolute Deviation. |
|
meanabs_risk_g |
Mean Absolute for Gain for Linear Loss scenarios. (Mean Absolute for Gain) = -Average Loss + Mean Absolute Deviation. |
|
meansquare |
Mean Square of Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios or Expected Matrix of Products. |
|
pm_dev |
Expected access of ( (Loss ) - (Average Loss )) over some fixed threshold. |
|
pm_dev_g |
Expected access of (- (Loss ) + (Average Loss )) over some fixed threshold. |
|
pm_pen |
Expected access of ( (Loss ) - (Average Loss )) over some fixed threshold. |
|
pm_pen_g |
Expected access of -( Loss ) over some fixed threshold. |
|
pm2_dev |
Expected squared access of ((Loss ) - (Average Loss )) over some fixed threshold.
|
|
pm2_dev_g |
Expected squared access of (-(Loss ) + (Average Loss )) over some fixed threshold. |
|
pm2_pen |
Expected squared Linear Loss in access of of some fixed threshold. |
|
pm2_pen_g |
Expected squared Linear -(Loss ) in access of of some fixed threshold. |
|
polynom_abs |
Sum of absolute values of components of a vector, i.e., L1 norm of a vector. |
|
pow_eut |
Power Utility function for Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
pr_dev |
Probability that (Loss)-(Average Loss) exceeds some fixed threshold. |
|
pr_dev_g |
Probability that -(Loss)+(Average Loss) exceeds some fixed threshold. |
|
pr_pen |
Probability that Linear Loss exceeds some fixed threshold. |
|
pr_pen_g |
Probability that Linear -(Loss ) exceeds some fixed threshold. |
|
quadratic |
Quadratic function |
|
st_dev |
Standard Deviation of Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
st_pen |
Root Squared Error of Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios or Expected Matrix of Products. By definition, it is an average of squared loss scenarios. |
|
st_risk |
(Standard Deviation of Linear Loss scenarios)+(Average of Linear Loss scenarios). It is calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
st_risk_g |
(Standard Deviation of Linear Loss scenarios)-(Average of Linear Loss scenarios). It is calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
|
var_comp_neg |
α*I -th value in the ordered ascending sequence of components of a -(I-dimensional vector), where 0≤α≤1; e.g., α=0.8, I=100, we order components of the -(vector) and take the element number α*I = 80 |
|
var_comp_pos |
Maximal (largest) component of a vector . |
|
var_dev |
Value-at-Risk for (Linear Loss ) - (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) , i.e., α% percentile of (Linear Loss) - (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) scenarios. |
|
var_dev_g |
Value-at-Risk for -(Linear Loss ) + (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) , i.e., α% percentile of -(Linear Loss) + (Average over Linear Loss scenarios) scenarios. |
|
var_risk |
Value-at-Risk for Linear Loss scenarios, i.e., α% percentile of Linear Loss scenarios. |
|
var_risk_g |
Value-at-Risk for -(Linear Loss ) scenarios, i.e., α% percentile of -(Linear Loss) scenarios. |
|
variance |
Variance of Linear Loss scenarios calculated with Matrix of Scenarios. |
